
The Atlantic Genealogy of Human Rights: Tracing the Dutch Origins of Roosevelt’s Four Freedoms and the Architecture of the United Nations
Franklin Roosevelt’s "Four Freedoms," articulated in 1941, trace their ideological roots to his ancestors' Dutch values of religious tolerance and collective security found in the 1579 Union of Utrecht. These principles were codified into the UN Charter and Universal Declaration of Human Rights, a legacy honored biennially in Zeeland, Netherlands.
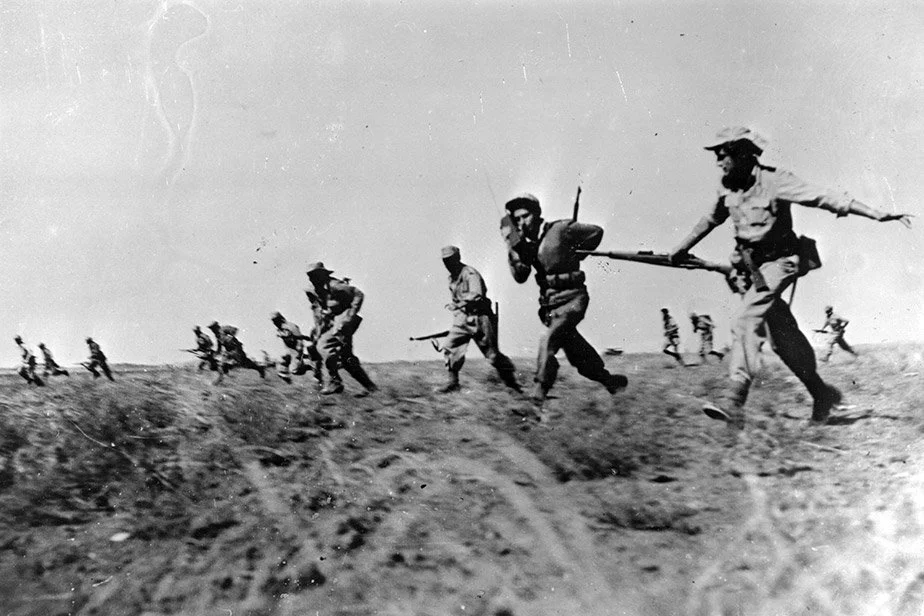

The War of 1948: A Geopolitical, Military, and Demographic Analysis of the Foundational Middle East Conflict
The 1948 War, known as the War of Independence or Nakba, evolved from a civil conflict into a regional war following Israel's independence. Israel's unified command defeated disjointed Arab armies, securing 78% of Mandatory Palestine. The conflict displaced approximately 700,000 Palestinians and precipitated a massive Jewish exodus from Arab nations.
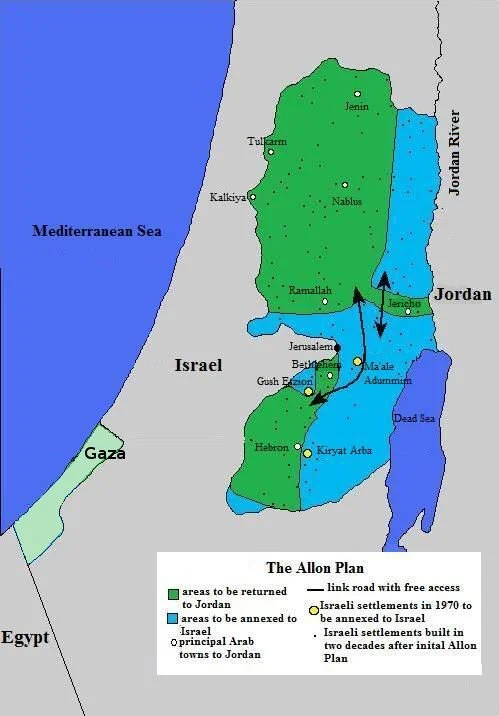
The Allon Plan: Strategic Doctrine, Territorial Compromise, and the Shaping of Israeli Borders (1967–Present)
The Allon Plan (1967) proposed that Israel annex the strategically vital Jordan Valley and Greater Jerusalem to create defensible borders. In exchange for peace, the densely populated West Bank mountain ridge would return to Jordanian rule, connected via a corridor at Jericho, thereby maximizing Israeli security while minimizing its Arab population.

The Geopolitical Phantom: A Comprehensive Analysis of the 1949 Armistice Lines ("The Green Line")
Established by the 1949 Armistice Agreements, the Green Line separates sovereign Israel from the occupied West Bank and Gaza. Although legally temporary and physically eroded by Israeli settlements and infrastructure, it remains the primary international reference point for future borders and the two-state solution.

The 1967 Six-Day War: A Comprehensive Geopolitical and Military Analysis
In June 1967, Israel launched a preemptive strike against Egypt, Jordan, and Syria. Achieving total air superiority, Israel rapidly captured the Sinai, West Bank, Gaza, and Golan Heights. This decisive victory reshaped the Middle East, establishing Israel as a regional power and initiating the ongoing occupation of Palestinian territories.

The 1967 Transformation: A Geopolitical and Legal History of the Occupied Palestinian Territories
In June 1967, Israel captured the West Bank, Gaza Strip, and Golan Heights, ending Jordanian and Egyptian rule. This established a military administration under Proclamation No. 2 and initiated the settlement enterprise. Simultaneously, East Jerusalem was de facto annexed , while hundreds of thousands of Palestinians were displaced in the "Naksa".

The Geopolitical and Legal Paradigm Shift of UN General Assembly Resolution 67/19: A Comprehensive Analysis
Adopted on November 29, 2012, UN Resolution 67/19 upgraded Palestine to "non-member observer State" status by a vote of 138-9. Opposed by the US and Israel, this legal pivot enabled Palestine to access the International Criminal Court and other treaties, fundamentally shifting its strategy from bilateral negotiations to international "lawfare".

The Status of Palestine in the United Nations System: A Comprehensive Legal and Diplomatic Assessment (December 2025)
As of December 2025, Palestine remains a UN Non-Member Observer State, blocked from full membership by a US Security Council veto. However, it exercises "enhanced" privileges, sits among members, and holds full membership in agencies like UNESCO. With 159 global recognitions, it functions diplomatically as a state despite formal limitations.

The Geopolitical and Legal Paradigm Shift of UN General Assembly Resolution 67/19: A Comprehensive Analysis
Adopted on November 29, 2012, UN Resolution 67/19 upgraded Palestine to "non-member observer State" status by a vote of 138-9. Opposed by the US and Israel, this legal pivot enabled Palestine to access the International Criminal Court and other treaties, fundamentally shifting its strategy from bilateral negotiations to international "lawfare".

From Stockholm to Rio: The 20-Year Evolution of Global Environmental Governance and the Genesis of Principle 27
Rio’s 27th principle marks the paradigm shift to "sustainable development," replacing Stockholm’s 1972 diagnostic framework. It serves as a procedural capstone, mandating good-faith cooperation to bridge North-South divides. It binds nations to continuously evolve international law to address complex global challenges.